Dependency Injection in ASP.NET Core
September 10, 2025
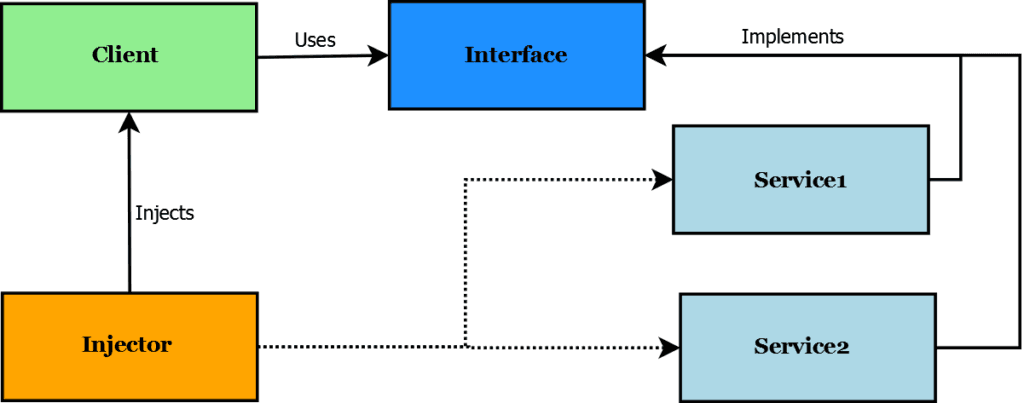
Introduction
Dependency Injection (DI) is a core feature of ASP.NET Core that promotes loose coupling and testability. In this post, we’ll explore how to use DI effectively.
Registering Services
ASP.NET Core’s built-in DI container allows you to register services in Program.cs.
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Builder;
using Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection;
var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args);
// Register services
builder.Services.AddScoped<IUserService, UserService>();
var app = builder.Build();
app.MapGet("/user/{id}", async (int id, IUserService userService) => {
var user = await userService.GetUserByIdAsync(id);
return user != null ? Results.Ok(user) : Results.NotFound();
});
app.Run();
public interface IUserService
{
Task<User> GetUserByIdAsync(int id);
}
public class UserService : IUserService
{
public async Task<User> GetUserByIdAsync(int id)
{
// Simulate database call
await Task.Delay(100);
return new User { Id = id, Name = "Jane Doe" };
}
}
public class User
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
}
Benefits of DI
- Testability: Easily mock dependencies for unit tests.
- Flexibility: Swap implementations without changing code.
- Maintainability: Cleaner and more modular code.
Conclusion
Using DI in ASP.NET Core allows you to build scalable and testable applications. Combine it with proper service lifetimes (transient, scoped, singleton) for optimal performance.